What
are the core services of vCenter server-
vCenter Server offers core services in the
following areas:
VM deployment
VM management
ESXi host
management
Resource management
for ESXi hosts and VMs
Template management
Scheduled tasks
Statistics and
logging
Alarms and event
management
vCenter Server Heartbeat:- A product available from
VMware. Using vCenter Server Heartbeat will automate both the process of
keeping the active and passive vCenter Server instances synchronized and the
process of failing over from one to another (and back again).
Can
a local user defined in a ESXi host connect to vCenter server using vSphare
client-
Although the vSphere Client supports authentication
of both vCenter Server and ESXi hosts, organizations should use a consistent
method for provisioning user accounts to manage their vSphere infrastructure
because local user accounts created on an ESXi host are not reconciled or
synchronized with the Windows or Active Directory accounts that vCenter Server
uses.
Which
version of vCenter Server you will use- What are advantages and disadvantages
of using each vCenter server editions-
In vSphere 5 vCenter Server now comes not only as
a Windows-based application but also as SuSE Linux-based virtual appliance. There
are advantages and disadvantages for each vertions:-
1>Preloaded additional services like Auto
Deploy, DHCP, TFTP, Syslog:-
2>
Administrators platform familiarities:-
3>Using Microsoft SQL Server for backend
database:-
4> Using vCenter server in Linked Mode
5>IPv6 Support:-
6> Running vCenter Server on a physical
system:-
7> Using vCenter Heartbeat:-
1>Preloaded
additional services like Auto Deploy, DHCP, TFTP, Syslog:-
The Linux-based virtual appliance comes preloaded with additional services like
Auto Deploy , Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), Trivial File Transfer
Protocol (TFTP), and Syslog. If you need these services on your network, you
can provide these services with a single deployment of the vCenter virtual
appliance.
With
the Windows Server–based version, these services are separate installations or
possibly even require separate VMs (or, worse yet, separate physical servers!).
2> Administrators platform familiarities:-
If your experience is primarily with Windows Server, the Linux underpinnings of
the vCenter virtual appliance are something with which you may not be familiar.
This introduces a learning curve that you should consider.
Conversely, if your experience is primarily with
Linux, then deploying a Windows Server–based application will require some
learning and acclimation for you and/or your staff.
3>Using
Microsoft SQL Server for backend database:-
If you need support
for Microsoft SQL Server, the Linux-based vCenter virtual appliance won’t work;
you’ll need to deploy the Windows Server–based version of vCenter Server.
However, if you are using Oracle or DB2, or if you are a small installation
without a separate database server, the vCenter Server virtual appliance will
work just fine (it has its own embedded database if you don’t have or don’t
need a separate database server).
4> Using
vCenter server in Linked Mode:-
If you need to use linked mode,
you must deploy the Windows Server–based version of vCenter Server. The vCenter
Server virtual appliance does not support linked mode.
5>IPv6
Support:-
If you need support for IPv6,
the vCenter Server virtual appliance does not provide that support; you must
deploy the Windows Server–based version.
6> Running
vCenter Server on a physical system:-
Because the vCenter Server
virtual appliance naturally runs only as a VM, you are constrained to that
particular design decision. If you want or need to run vCenter Server on a
physical system, you cannot use the vCenter Server virtual appliance.
7> Using
vCenter Heartbeat:-
If you want to use vCenter
Heartbeat to protect vCenter Server from downtime, you’ll need to use the
Windows Server–based version of vCenter Server.
What
is the minimum requirement of installing a vCenter server?
Two
64-bit CPUs or a single dual-core 64-bit CPU.
2 GHz processor or faster.
3 GB of RAM or more.
3 GB of free disk space.
A
network adapter (Gigabit Ethernet strongly recommended).
A supported version of Windows (Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2003 R2,
Windows Server 2008, or Windows Server 2008 R2); vCenter Server 5 requires a
64-bit version of Windows.
What
are the databases supported by vCenter server-
Although vCenter Server is the application that
performs the management of your ESXi hosts and VMs, vCenter Server uses a
database for storing all of its configuration, permissions, statistics, and
other data.
vCenter server supports following databases:-
IBM DB2- 9.5, 9.7
Oracle 10g R2-- 11g R1-- 11g R2
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Express (bundled with vCenter Server)
Microsoft SQL Server 2005- 2008
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2
vCenter server Linked Mode Group:-
Multiple instances of vCenter Server that share
information among them.
In
what situation you need a separate database server for vCenter?
[a single
(1) vCenter Server with fewer than five (5) Esxi hosts or fewer than 50 VMs],
What
are the services installed to facilitate the operation of vCenter Server-
vCenter Inventory Service.
VMware vCenter Orchestrator
Configuration (supports the Orchestrator workflow engine.
VMware VirtualCenter Management Web
services.
VMware VirtualCenter Server is the
core of vCenter Server and provides centralized management of ESX/ESXi hosts
and VMs.
VMware vSphere Profile-Driven Storage
Service.
VMwareVCMSDS is the Microsoft ADAM
instance that supports multiple vCenter Server instances in a linked mode group
and is used for storing roles and permissions. Note that ADAM is used for
storing roles and permissions both in stand-alone installations as well as
installations with a linked mode group.
What are the limitations of Using SQL Server
2008 Express Edition?
SQL Server 2008 Express Edition is the minimum
database available as a backend to the Windows Server–based version of vCenter
Server.
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Express Edition has
physical limitations that include the following:
One CPU maximum
1 GB maximum of
addressable RAM
4 GB database
maximum
How
do you protect vCenter server and make it highly available-
First> vCenter Server Heartbeat:-
Second> Standby physical vCenter
server:-
Third> keep
the standby vCenter Server system as a VM:-
First> vCenter Server
Heartbeat:-
A product available from VMware. Using vCenter
Server Heartbeat will automate both the process of keeping the active and
passive vCenter Server instances synchronized and the process of failing over
from one to another (and back again).
Second> Standby physical
vCenter server:-
If the vCenter Server computer is a physical
server, one way to provide availability is to create a standby vCenter Server
system that you can turn on in the event of a failure of the online vCenter
Server computer. After failure, you bring the standby server online and attach
it to the existing SQL Server database, and then the hosts can be added to the
new vCenter Server computer. In this approach, you’ll need to find mechanisms
to keep the primary and secondary/standby vCenter Server systems synchronized.
Third>
keep the standby vCenter Server system as a VM:-
A variation on that approach is to keep the
standby vCenter Server system as a VM. You can use physical-to-virtual (P2V)
conversion tools to regularly “back up” the physical vCenter Server instance to
a standby VM. This method reduces the amount of physical hardware required and
leverages the P2V process as a way of keeping the two vCenter Servers
synchronized. Obviously, this sort of approach is viable for a Windows
Server–based installation on a physical system but not applicable to the
virtual appliance version of vCenter Server.
How
to protect “vCenter” backend database server-
1ST) Database
Cluster:-
2ND) SQL log shipping to create a
database replica on separate system:-
3RD) Daily backup strategy which
includes full, differential and transaction log backup:-
Protecting Backend database server-
1ST)
Database Cluster:- The heart of the vCenter Server
content is stored in a backend database. Any good disaster-recovery or
business-continuity plan must also include instructions on how to handle data
loss or corruption in the backend database, and the separate database server (if
running on a separate physical computer or in a separate VM) should be designed
and deployed in a resilient and highly available fashion. This is especially
true in larger environments. You can configure the backend database on a
cluster.
2ND) SQL log shipping to create a
database replica:-
Other options might include using SQL log
shipping to create a database replica on a separate system.
3RD)
Daily backup strategy which includes full, differential
and transaction log backup:-
You should strengthen your database backup
strategy to support easy recovery in the event of data loss or corruption.
Using the native SQL Server tools, you can create a backup strategy that
combines full, differential, and transaction log backups. This strategy allows
you to restore data up to the minute when the loss or corruption occurred.
What
is "Simple Recovery" model and what is "Full Recovery"
model-
Simple recovery-delete transaction logs.
Full recovery-keeps transaction logs for full
database recovery
If your SQL Server database is configured for the
Full recovery model, the installer suggests reconfiguring the vCenter Server
database into the Simple recovery model. What the warning does not tell you is
that doing this means that you will lose the ability to back up transaction
logs for the vCenter Server database. If you leave the database set to Full
recovery, be sure to work with the database administrator to routinely back up
and truncate the transaction logs. By having transaction log backups from a
database in Full recovery, you have the option to restore to an exact point in
time. if any type of data corruption occur. If you alter the recovery model as
suggested, be sure you are making consistent full backups of the database, but
understand that you will be able to recover only to the point of the last full
backup because transaction logs will be unavailable.
Do
we need IIS on vCenter server-
Despite the fact that vCenter Server is
accessible via a web browser, it is not necessary to install Internet
Information Services on the vCenter Server computer. vCenter Server is accessed
via a browser that relies on the Apache Tomcat web service and that is
installed as part of the vCenter Server installation. IIS should be uninstalled
because it can cause conflicts with Apache Tomcat.
What
are the memory requirement of vCenter server-
Host profile:- Host profile is a collection of
all the various configuration settings available for an ESXi host. By attaching
a host profile to an ESXi host, you can (i) compare the compliance or
non-compliance of that host with the settings outlined in the host profile. It provides
administrators with a way to not only to verify consistent settings across all
the ESXi hosts but also to (ii) quickly and easily apply settings to new ESXi
hosts.
What is SSO- Single Sign On
is an authentication and identity management service. It allows
administrators and the various vSphere software components to communicate with
each other through a secure token exchange mechanism, instead of requiring each
component to authenticate a user separately with a directory service like
Active Directory.
VMware Lookup Service:-
The vCenter Sign-On installer also deploys the "VMware Lookup Service"
on the same address and port. This Lookup Service enables different components
of vSphere to find one another in a secure way.
In Details:-
What is vCenter server Linked Mode Group-
Multiple instances
of vCenter Server that share information among them are referred to as a "linked mode group".
If you need more ESXi hosts or more VMs than a
single vCenter Server
instance can handle, or if for whatever other
reason you need more than one instance of vCenter Server, you can install
multiple instances of vCenter Server and have those instances share inventory
and configuration information for a centralized view of all the virtualized
resources across the enterprise.
In a linked mode environment, there are multiple
vCenter Server instances, and each of the instances has its own set of hosts,
clusters, and VMs. However, when a user logs into a vCenter Server instance
using the vSphere Client, that user sees all the vCenter Server instances where
he or she has permissions assigned. This allows a user to perform actions on
any ESXi host managed by any vCenter Server within the linked mode group.
vCenter Server linked mode uses Microsoft ADAM to
replicate information between the instances. The replicated
information includes the following:
Connection
information (IP addresses and ports)
Certificates and
thumbprints
Licensing
information
User roles and
permissions
In a linked mode environment,
the vSphere Client shows all the vCenter Server instances for which a user has
permission
What
are the prerequisites of installing vCenter server in a linked mode group-
Before you install additional vCenter Server
instances, you must verify the following prerequisites:-
Link mode servers should be Member of same domain or a trusted domain:-
DNS
name must match with the vcenter servers server name-
Lonked mode servers Cannot
be DC or terminal server:-
Cannot combine with earlier
versions of vcenter vertions:-
Must have its own backend
database:-
Member of same domain or a trusted
domain:-All
computers that will run vCenter Server in a linked mode group must be members
of a domain. The servers can exist in different domains only if a two-way trust
relationship exists between the domains.
DNS name must match with the vCenter server name:- DNS must be operational. Also,
the DNS name of the servers must match the server name.
Cannot be DC or terminal server:-The servers that will run
vCenter Server cannot be domain controllers or terminal servers.
Cannot combine with earlier versions:-
You cannot combine
vCenter Server 5 instances in a linked mode group with earlier versions of
vCenter Server.
Must have its own backend database:- Each vCenter Server instance
must have its own backend database, and each database must be configured as
outlined earlier with the correct permissions. The databases can all reside on
the same database server, or each database can reside on its own database
server.
How do you modify vCenter server linked mode
configuration?
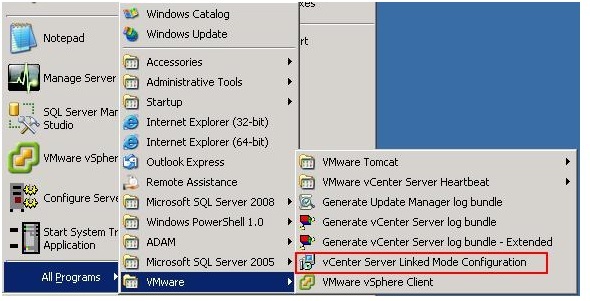
1. Log into the vCenter Server
computer as an administrative user, and run vCenter Server Linked Mode
Configuration from the Start=>All Programs=>VMware Menu.
2. Click Next at the Welcome To The
Installation wizard For VMware vCenter Server screen.
3. Select Modify Linked Mode Configuration, and click
Next.
What is host profile-
A host profile is essentially a collection of all
the various configuration settings for an ESXi host. This includes settings
such as NIC assignments, virtual switches, storage configuration, date and
time, and more. By attaching a host profile to an ESXi host, you can then
compare the compliance of that host with the settings outlined in the host
profile. If the host is compliant, then you know its settings are the same as
the settings in the host profile. If the host is not compliant, then you can
enforce the settings in the host profile to make it compliant. This provides
administrators with a way not only to verify consistent settings across ESXi
hosts but also to quickly and easily apply settings to new ESXi hosts.
To create a new profile, you must either create
one from an existing host or import a profile that was already created
somewhere else. Creating a new profile from an existing host requires only that
you select the reference host for the new profile. vCenter Server will then
compile the host profile based on that host’s configuration.
Host profiles don’t do anything until they are attached to ESXi
hosts. So attach the host profile to the new ESXi host. Then Check Compliance
with the host. If an ESXi host is found noncompliant with the settings in a
host profile, you can then place the host in maintenance mode and apply the
host profile. When you apply the host profile, the settings found in the host
profile are enforced on that ESXi host to bring it into compliance.
What
are the configuration requirements of using SQL server as a backend database of
vCenter server-
Connecting vCenter Server to a
Microsoft SQL Server database, like the Oracle implementation, requires a few
specific configuration tasks, as follows:-
Both Windows and
mixed mode authentication are supported:-
A new database for
each vCenter Server:-
SQL login that has
full access to the database:-
Appropriate permissions by mapping the SQL login to the dbo user:-
SQL login must also be set as the owner of the database:-
Must also have dbo
(db_owner) privileges on the MSDB database when installing:-
Your
manager has asked you to prepare an overview of the virtualized environment.
What tools in vCenter Server will help you in this task-
vCenter Server can export topology maps in a
variety of graphics formats. The topology maps, coupled with the data found on
the Storage
Views, Hardware Status, and Summary tabs should provide
enough information for your manager
What
is SSO? what are its role in vCenter server-
The vCenter Single Sign On is an authentication
and identity management service which makes the VMware cloud infrastructure
platform more secure. It allows administrators and the various vSphere software
components to communicate with each other through a secure token exchange
mechanism, instead of requiring each component to authenticate a user
separately with a directory service like Active Directory.
Roles:-
For the first installation of
vCenter Server with vCenter Single Sign-On, you must install all three
components, Single Sign-On Server, Inventory Service, and vCenter Server, in
the vSphere environment. In subsequent installations of vCenter Server in your
environment, you do not need to install Single Sign-On. One Single Sign-On
server can serve your entire vSphere environment. After you install vCenter
Single Sign-On once, you can connect all new vCenter Server instances to the
same authentication server. However, you must install a Inventory Service
instance for each vCenter Server instance.
The vCenter Sign-On installer also
deploys the VMware Lookup Service on the same address and port. The Lookup
Service enables different components of vSphere to find one another in a secure
way. When you install vCenter Server components after vCenter Single Sign-On,
you must provide the Lookup Service URL. The Inventory Service and the vCenter
Server installers ask for the Lookup Service URL and then contact the Lookup
Service to find vCenter Single Sign-On. After installation, the Inventory
Service and vCenter Server are registered in Lookup Service so other vSphere
components, like the vSphere Web Client, can find them.








